Data Structure(3) - Linked List
What is the Linked List?
Linked List is also a kind of Dynamic Array but it doesn’t use index. The object type in the linked list is LinkedListNode. Node has referecnes about next node and previous node. Also, LinkedList point to a list. This means if I declare 2 linked list and one of them points to a list and another one points the first linked list, they point to same the list. Let’s see the example.
1
2
LinkedList<int> list1 = new LinkedList<int>();
LinkedList<int> list2 = list1;
In this case, don’t forget the list 1 and 2 point to the same list!
How to Declare and Add Item into Linked List?
As you can see the example before, we can declare a linked list with data type. And, we need to use AddLast() method to add a new node to linked list.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
LinkedList<int> list1 = new LinkedList<int>();
LinkedList<string> list2 = new LinkedList<string>();
list1.AddLast(1);
list1.AddLast(2);
// list1 = (1) - (2)
// if you want to add a node into the first you can use `AddFirst()`
list2.AddFirst("World!");
list2.AddFirsst("Hello, ");
// list2 = ("Hello, ") - ("World!")
Methods
Let’s see the example methods for linked list!
Remove / RemoveFirst / RemoveLast
If you want to remove a node in linked list, you can use Remove() method. Don’t forget it is going to remove the first node. We can remove first node or last node using RemoveFirst() or RemoveLast().
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
LinkedList<int> list = new LinkedList<int>();
list.AddLast(1);
list.AddLast(2);
list.AddLast(4);
list.AddLast(3);
list.AddLast(4);
list.AddLast(5);
list.Remove(4); // list = (1) - (2) - (3) - (4) - (5)
list.Remove(1); // list = (2) - (3) - (4) - (5)
// remove first and last node
list.RemoveFirst(); // list = (3) - (4) - (5)
list.RemoveLast(); // (3) - (4)
Find
There would be a situation that we need to check if the linked list has a node with exact value. In this case, we can use Find() method.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
LinkedList<int> list = new LinkedList<int>();
list.AddLast(1);
list.AddLast(2);
list.AddLast(3);
list.AddLast(4);
list.AddLast(5);
// if the linked list has a node with a value of 6, it will return a LinkedListNode. if not, check will be null
LinkedListNode<int> check = list.Find(6);
if(check == null) {
Console.WriteLine("Check is empty!!!!")
}else {
Console.WriteLine("Check's value is " + check)
}
// console
// -> Check is empty!!!!
Example Problem
Let’s solve Merge Two Sorted Lists!
Problem Description:
You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists list1 and list2. Merge the two lists into one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists. Return the head of the merged linked list.
Example 1:
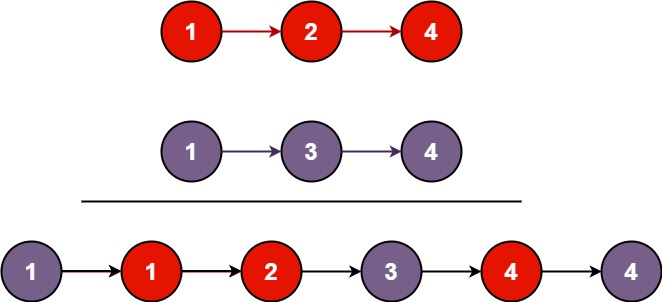
Input: list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]
Example 2: Input: list1 = [], list2 = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: list1 = [], list2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in both lists is in the range [0, 50].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Both list1 and list2 are sorted in non-decreasing order.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public class Solution {
public ListNode MergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// if one of the lists is null, we just need to return another list
if(list1 == null) return list2;
if(list2 == null) return list1;
// result points a first node in a list
ListNode result = new ListNode();
// current works as a cursor and points the same node with result
ListNode current = result;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null)
{
int value = 0;
if(list1.val <= list2.val)
{
value = list1.val;
// by using list1.next, we can go to the next node in list1
list1 = list1.next;
}
else
{
value = list2.val;
// by using list2.next, we can go to the next node in list2
list2 = list2.next;
}
current.next = new ListNode(value);;
// by using current.next, we can change the cursor to the next node
current = current.next;
}
// fill the list with the rest node in the list
if(list1 == null) current.next = list2;
else if(list2 == null) current.next = list1;
// it is because the result still points the first node, we can get all the nodes using result.next
return result.next;
}
}