Data Structure(11) - Heap
What is Heap?
Heap is a kind of Tree Structure. There are 2 types of Heap which are Max Heap and Min Meap. Both Heap have a rule that the parent node must be larger/less than children nodes.
Let me show you examples. 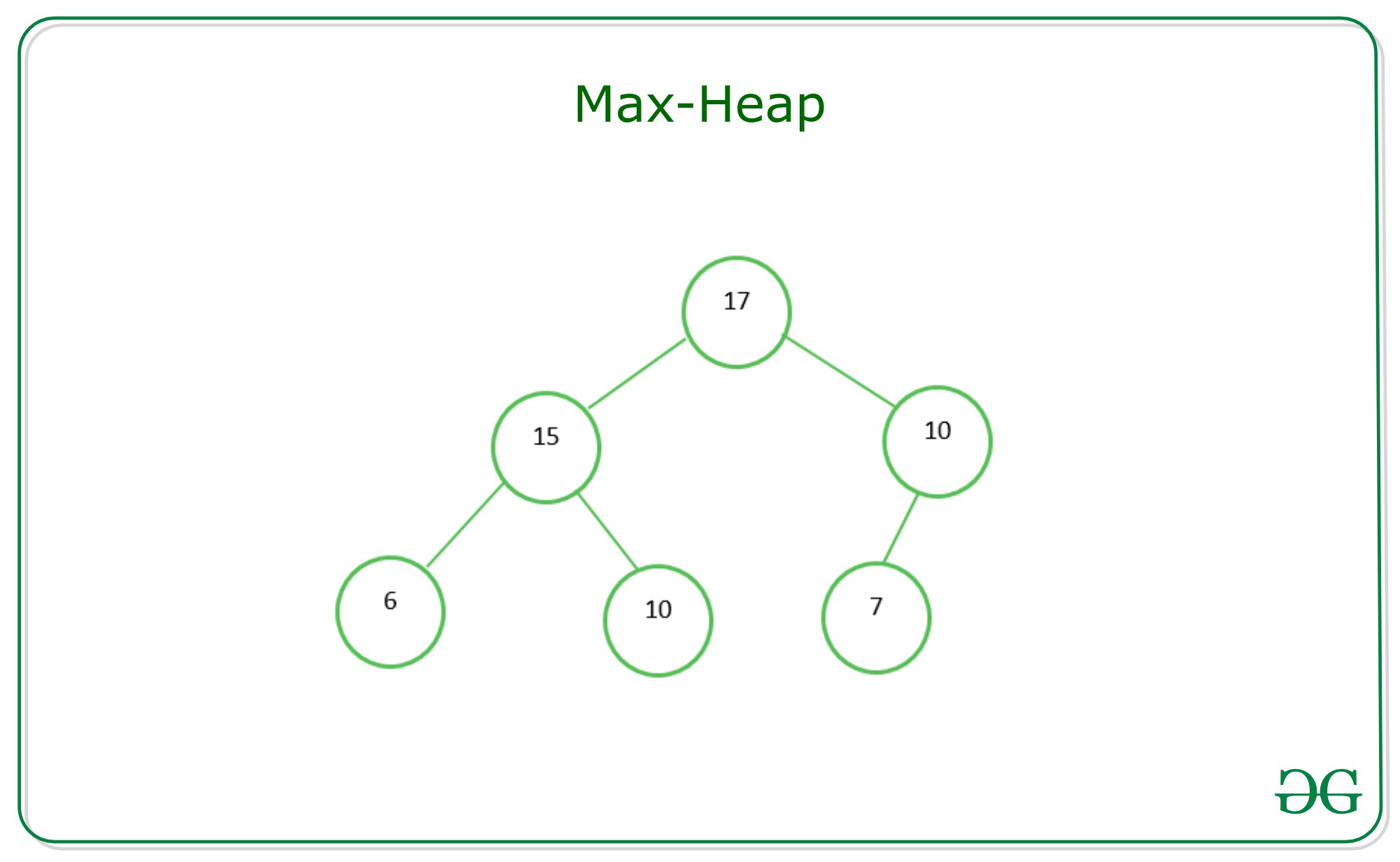
This is an example for Max Heap. The head node is the largest number in this tree.
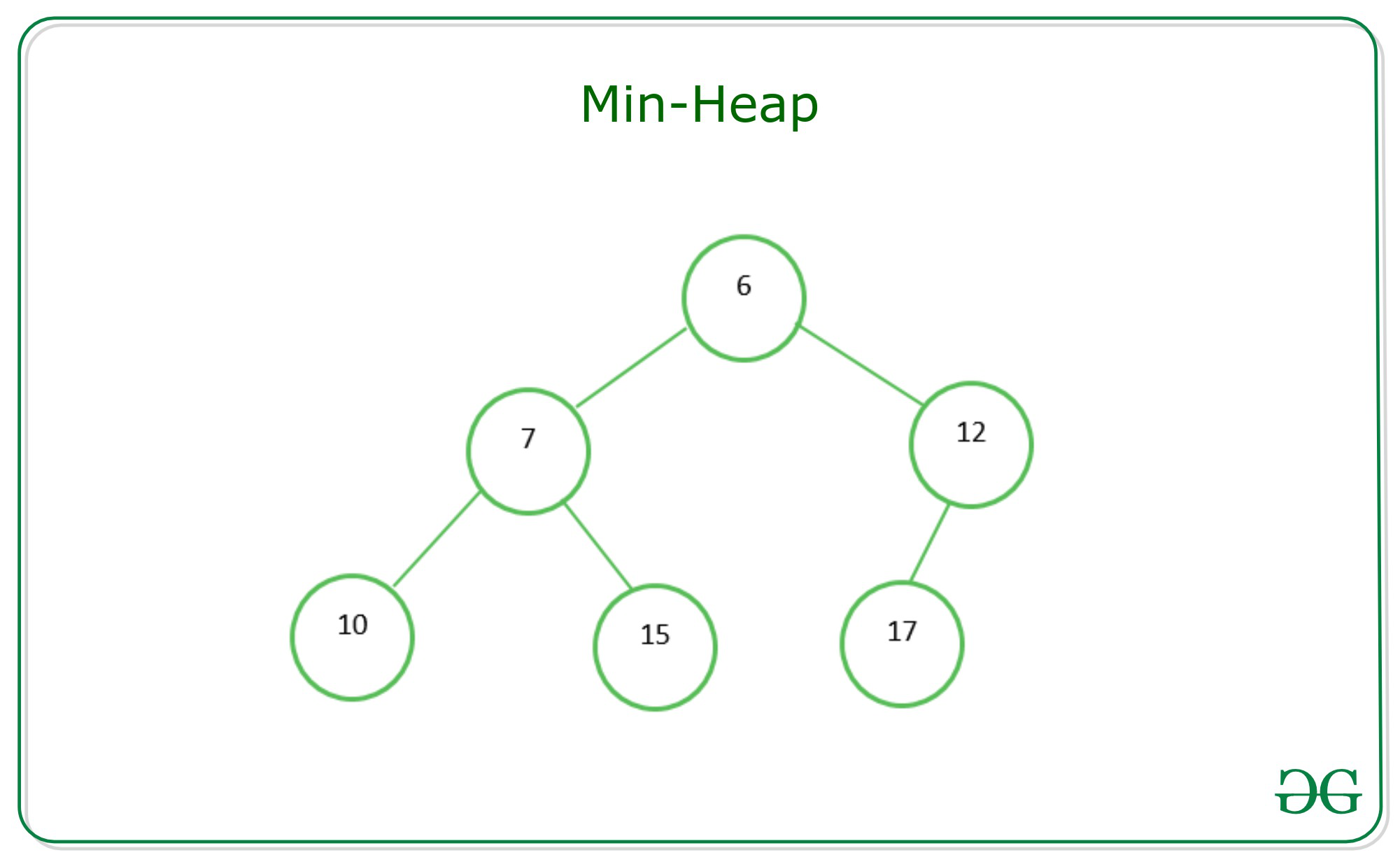
This is an example for Min Heap. The head node is the smallest number in this tree.
Priority Queue
Priority Queue is used similar as Queue. But whenever you enqueue a value into Priority Queue, it will be sorted automatically. You can add comparer to make the Priority Queue as a Max Heap or Min Heap.
There is a class for Priority Queue in C# applies after .NET 6. Unlike Java’s Priority Queue will sort the Priority Queue by value, C# sorts Priority Queue by Priority that you entered.
How to Declare and Use a Priority Queue?
Priority Queue is also one of Dynamic Array so you can just use Enqueue method. But when you want to enqueue a value, you need to include the priority of the value.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// first int variable is value and second one is priority.
// the default order is ascending.
PriorityQueue<int, int> pq = new PriorityQueue<int, int>();
pq.Enqueue(1, 1);
pq.Enqueue(2, 2);
while(pq.Count > 0) {
Console.WriteLine(pq.Dequeue());
}
Console: result
1
2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// if you want to change the order to descending,
// you need to add comparer like below
PriorityQueue<int, int> pq = new PriorityQueue<int, int>(Comparer<int>.Create((x, y) => y - x));
pq.Enqueue(1, 1);
pq.Enqueue(2, 2);
while(pq.Count > 0) {
Console.WriteLine(pq.Dequeue());
}
Console: result
2
1
Example Problem
Let’s solve Relative Ranks!
Problem Description:
You are given an integer array score of size n, where score[i] is the score of the ith athlete in a competition. All the scores are guaranteed to be unique.
The athletes are placed based on their scores, where the 1st place athlete has the highest score, the 2nd place athlete has the 2nd highest score, and so on. The placement of each athlete determines their rank:
The 1st place athlete’s rank is “Gold Medal”.
The 2nd place athlete’s rank is “Silver Medal”.
The 3rd place athlete’s rank is “Bronze Medal”.
For the 4th place to the nth place athlete, their rank is their placement number (i.e., the xth place athlete’s rank is “x”).
Return an array answer of size n where answer[i] is the rank of the ith athlete.
Example 1:
Input: score = [5,4,3,2,1]
Output: [“Gold Medal”,”Silver Medal”,”Bronze Medal”,”4”,”5”]
Explanation: The placements are [1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th].
Example 2:
Input: score = [10,3,8,9,4]
Output: [“Gold Medal”,”5”,”Bronze Medal”,”Silver Medal”,”4”]
Explanation: The placements are [1st, 5th, 3rd, 2nd, 4th].
Constraints:
n == score.length
1 <= n <= 104
0 <= score[i] <= 106
All the values in score are unique.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public class Solution {
public string[] FindRelativeRanks(int[] score) {
// declare an array with same length with input array
// to save and return sorted score.
string[] result = new string[score.Length];
// Add Comparer to sort it by descending
PriorityQueue<int, int> highestScore = new PriorityQueue<int, int>(Comparer<int>.Create((x, y) => y - x));
// enqueue index as a value and score as a prority
for(int i = 0; i < score.Length; i++) {
highestScore.Enqueue(i, score[i]);
}
// save result into result array
for(int i = 0; i < score.Length; i++) {
int index = highestScore.Dequeue();
if(i == 0) {
result[index] = "Gold Medal";
}else if (i == 1) {
result[index] = "Silver Medal";
}else if (i == 2) {
result[index] = "Bronze Medal";
}else {
result[index] = (i + 1).ToString();
}
}
return result;
}
}